Liver Cancer
- Home / Dr. Uma Dangi
- Gastrointestinal cancers
- Colon Cancer
- Rectal Cancer
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Stomach Cancer
- Liver Cancer
- Gall Bladder Cancers
Liver Cancer
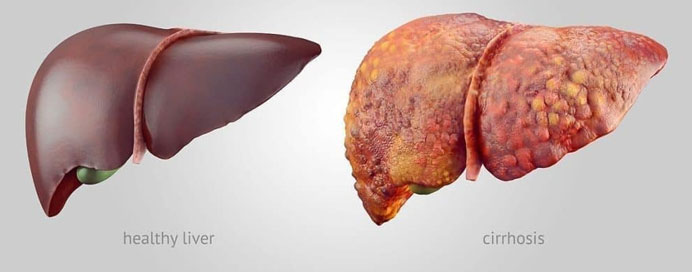
Liver cancer, also known as hepatocellular carcinoma, is a serious and often aggressive malignancy that originates in the cells of the liver. It is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths globally. Chronic liver diseases, such as cirrhosis, due to factors like hepatitis B or C infection, excessive alcohol consumption, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, significantly increase the risk of developing liver cancer. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and jaundice. Diagnosis involves imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRIs, and biopsy for confirmation. Treatment options for liver cancer depend on the cancer's stage and may include surgery, liver transplant, ablation therapy, chemotherapy, or targeted therapies. The prognosis for liver cancer is often challenging, as it is frequently diagnosed at advanced stages when treatment options are limited. Prevention through vaccination against hepatitis, lifestyle changes, and regular medical check-ups for those at risk are crucial in the fight against liver cancer.
