Lymphoma
- Home / Dr. Uma Dangi
- Blood Cancers
- Lymphoma
- Multiple Myeloma
- Leukemia
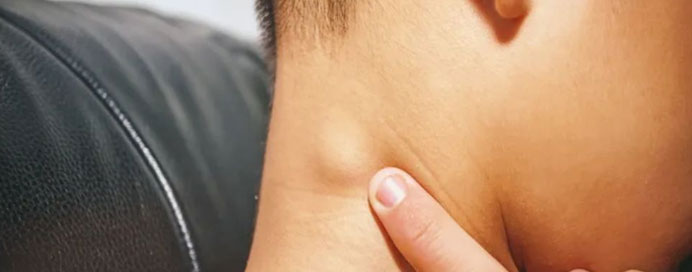
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system, a crucial part of the body's immune system. It can be broadly categorized into two main types: Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Hodgkin lymphoma is characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, while non-Hodgkin lymphoma comprises a diverse group of lymphomas with various subtypes. Lymphomas typically develop when lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, undergo abnormal growth and accumulate in lymph nodes or other lymphoid tissues. Common symptoms include swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Diagnosis involves a combination of imaging studies, biopsy, and other laboratory tests. Treatment varies depending on the specific type and stage of lymphoma but often includes chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy, and, in some cases, stem cell transplantation. Advances in understanding the molecular basis of lymphomas have led to more targeted and personalized treatment approaches, contributing to improved outcomes for many patients. Early detection and accurate diagnosis remain crucial factors in effectively managing lymphoma.
