Uterine Cancers
- Home / Dr. Uma Dangi
- Women's Cancers
- Breast Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Cervical Cancer
- Uterine Cancers
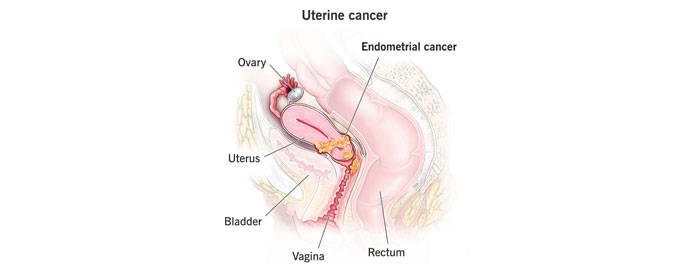
Uterine Cancers
Uterine cancer, also known as endometrial cancer, begins in the lining of the uterus (endometrium) and is the most common cancer of the female reproductive system. This cancer typically affects postmenopausal women, although it can also occur in premenopausal women. Prolonged exposure to estrogen without the counterbalance of progesterone is a key risk factor, making conditions such as obesity, hormonal imbalances, and certain medications potential contributors. Uterine cancer is often characterized by abnormal vaginal bleeding, which may include postmenopausal bleeding or irregular menstrual cycles. Diagnosis involves a combination of imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI, and endometrial biopsy. Treatment options depend on the cancer's stage and may include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Prognosis for uterine cancer is generally favorable, especially when diagnosed early. As with many cancers, awareness of risk factors and regular gynecological check-ups play crucial roles in early detection and successful management.
